The modern business landscape thrives on a diverse array of applications and systems that work together to ensure operational efficiency. Seamlessly integrating these components has become a crucial aspect of business success. Integration solutions play a vital role in enabling the smooth flow of data between applications, databases, and services, ultimately leading to streamlined processes and increased productivity.
Among the prominent integration solutions available today, iPaaS and ESB (Enterprise Service Bus) have gained significant popularity. This article delves into a comprehensive exploration of iPaaS and ESB, highlighting their unique features, benefits, and challenges. By the end, you will gain valuable insights to determine which solution aligns best with your business requirements.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!
Understanding iPaaS in Today’s Modern Digital Age
In today’s modern digital age, where technology has become the backbone of businesses, efficient and seamless integration of applications and systems has become a necessity. This is where iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) emerges as a powerful solution.
iPaaS refers to a cloud-based platform that offers a comprehensive set of tools and services to facilitate the integration of various applications, databases, and systems. It provides a centralized approach to integration, allowing businesses to connect and manage data flows between cloud-based and on-premises applications effortlessly.
The significance of iPaaS in today’s digital landscape cannot be overstated. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud-based applications and services, the need for efficient integration becomes paramount. iPaaS serves as a bridge that brings these disparate systems together, ensuring smooth data exchange and synchronization.
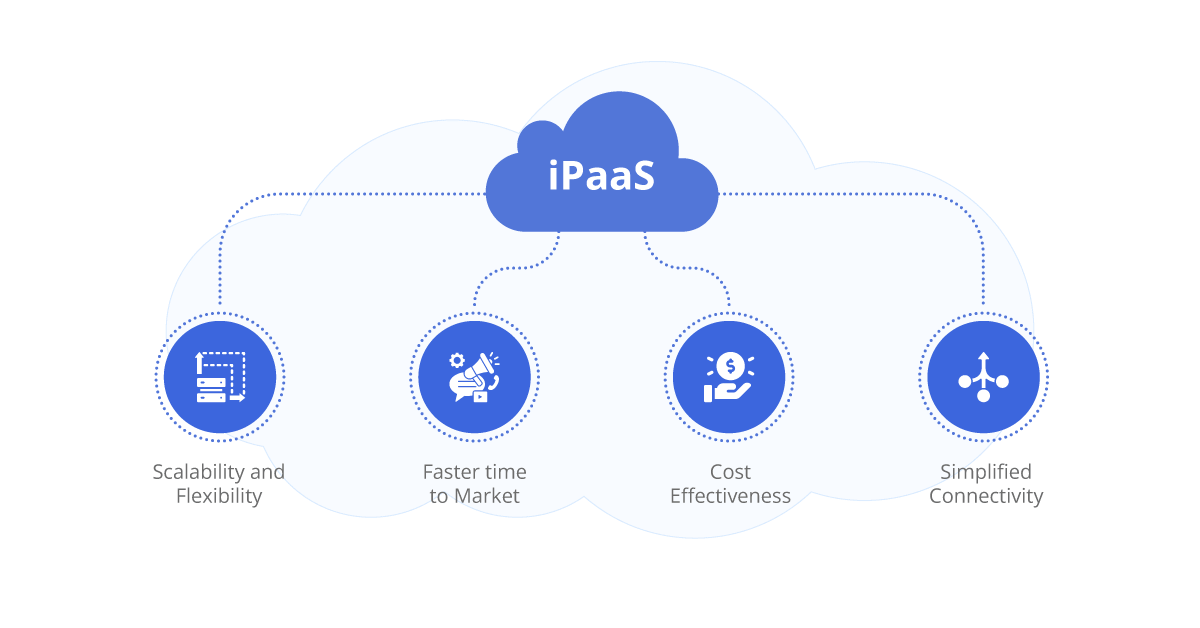
Benefits of iPaaS
Scalability and flexibility: iPaaS solutions are designed to handle the growing demands of businesses, providing scalable infrastructure and flexible deployment options. This allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing integration needs as they expand or introduce new applications.
Faster time to market: With iPaaS, businesses can accelerate the integration process by leveraging pre-built connectors and templates, reducing development time and effort. This enables faster deployment of new applications and services, giving companies a competitive edge in the market.
Cost-effectiveness: iPaaS eliminates the need for extensive hardware investments and infrastructure maintenance, as it operates in the cloud. This significantly reduces upfront costs and ongoing expenses associated with managing integration infrastructure.
Simplified connectivity: iPaaS platforms offer a wide range of connectors and APIs, enabling seamless connectivity between different applications and systems. This simplifies the integration process and allows businesses to integrate with various cloud-based and on-premises solutions.
Use cases and examples
Cloud application integration: A company utilizing multiple cloud-based applications, such as CRM, ERP, and marketing automation, can leverage iPaaS to integrate these systems and enable seamless data exchange. For example, an iPaaS platform such as Aonflow can automate the flow of customer data from the CRM system to the marketing automation tool, ensuring synchronized customer information.
Data synchronization and consolidation: iPaaS can be used to aggregate data from various sources and consolidate it into a centralized data repository. This enables businesses to gain a holistic view of their data, facilitating better decision-making. For instance, an e-commerce company can use iPaaS to sync data from online sales channels, inventory management systems, and accounting software to maintain accurate stock levels and generate real-time sales reports.
Workflow automation: iPaaS platforms offer workflow automation capabilities, allowing businesses to automate repetitive tasks and streamline business processes. For example, an HR department can use iPaaS to automate employee onboarding workflows, integrating HRIS, payroll, and benefits systems to ensure a seamless and efficient onboarding experience.
Challenges of iPaaS
Security and data privacy concerns: As iPaaS involves sharing and storing data in the cloud, businesses must carefully evaluate the security measures and data privacy policies of their chosen iPaaS provider. Confidential or sensitive data may require additional security measures or on-premises integration solutions.
Potential vendor lock-in: Businesses should consider the potential risks associated with vendor lock-in when opting for iPaaS. It is important to assess the platform’s flexibility and the ease of transitioning to alternative solutions if needed.
Exploring ESB
ESB, or Enterprise Service Bus, is an integration middleware that enables communication between different applications and services in a distributed environment. ESB acts as a central hub for message routing, transformation, and protocol mediation, ensuring reliable data delivery and interoperability between systems.
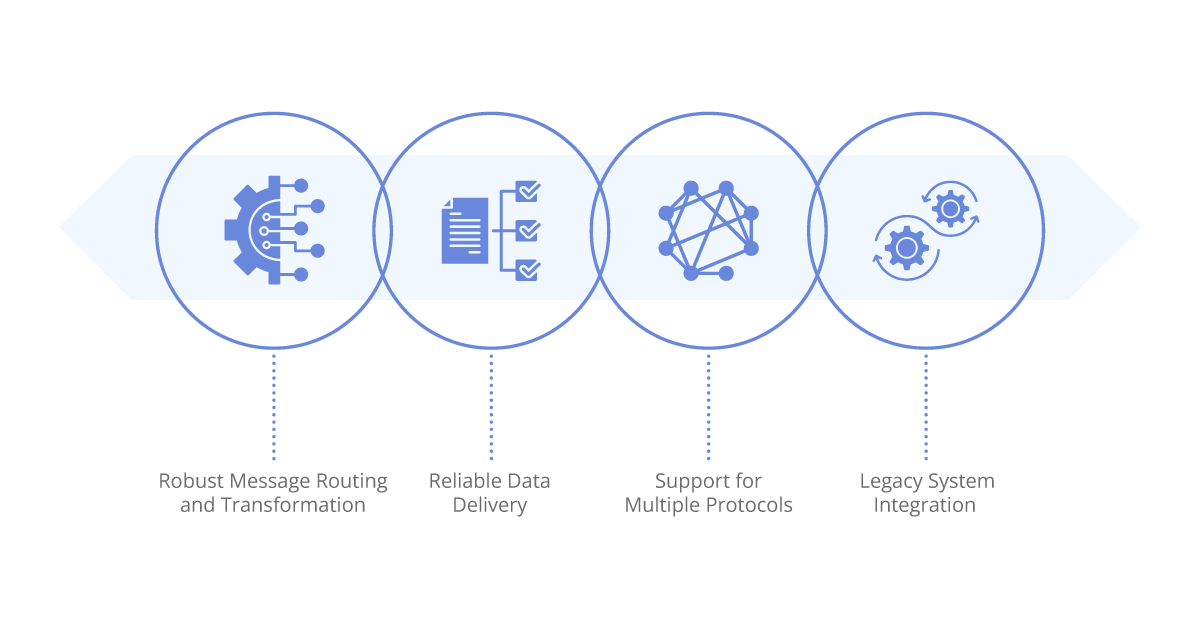
Benefits of ESB
Robust message routing and transformation: ESB provides powerful routing capabilities, enabling complex message routing scenarios based on content, destination, or predefined rules. It also facilitates message transformation, allowing data to be translated from one format to another, ensuring compatibility between systems.
Reliable data delivery: ESB ensures the reliable delivery of messages between applications, even in the event of system failures or network interruptions. It provides mechanisms such as guaranteed message delivery, message persistence, and error handling, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
Support for multiple protocols: ESB supports various communication protocols, such as HTTP, SOAP, JMS, and FTP, allowing seamless integration between systems using different protocols. This makes ESB suitable for heterogeneous environments with diverse technology stacks.
Legacy system integration: ESB is well-suited for integrating legacy systems with modern applications and services. It can act as a bridge between older systems and newer technologies, facilitating the migration process and ensuring smooth interoperability.
Use cases and examples
Enterprise application integration: ESB is commonly used for integrating large-scale enterprise applications, such as ERP, CRM, and SCM systems. For example, an organization can use ESB to connect its CRM system with the ERP system to enable real-time synchronization of customer data, orders, and inventory levels.
Service-oriented architecture (SOA): ESB plays a crucial role in implementing SOA, where services are loosely coupled and communicate through standardized interfaces. ESB acts as the backbone for service interactions, providing a flexible and scalable architecture for integrating and orchestrating services.
B2B integration: ESB facilitates seamless integration with external partners and suppliers, enabling smooth B2B communication. For instance, an e-commerce company can leverage ESB to integrate with third-party logistics providers for order fulfillment, ensuring efficient supply chain management.
Aonflow is the leading integration platform.
You can kick-start by integrating your first-ever workflow in just a matter of minutes.
Challenges of ESB
Complexity and learning curve: ESB implementations can be complex, requiring expertise in integration technologies and patterns. Organizations need to invest in skilled resources or external consultants to design, develop, and maintain the ESB infrastructure effectively.
Maintenance and scalability issues: ESB infrastructure requires ongoing maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal performance. Scaling an ESB solution can also be challenging, particularly when handling high message volumes or adding new systems to the integration landscape.
iPaaS vs ESB: Choosing the Right Solution
When deciding between iPaaS and ESB, businesses should consider several factors to make an informed decision:
Integration requirements: Assess the complexity of your integration needs, including the number and types of systems to be integrated, data volumes, and required workflows. iPaaS is well-suited for cloud-based integrations and simpler use cases, while ESB is ideal for complex enterprise-wide integration scenarios.
Scalability and future growth: Consider your business’s growth projections and scalability requirements. iPaaS offers elastic scalability, allowing businesses to adjust resources based on demand, whereas ESB may require additional infrastructure investments to accommodate future growth.
Budget and cost considerations: Evaluate the upfront costs, ongoing expenses, and return on investment (ROI) of each solution. iPaaS generally requires less upfront investment and is more cost-effective for smaller-scale integrations. ESB may involve higher upfront costs but offers greater flexibility and customization options.
IT infrastructure and existing systems: Analyze your current IT landscape and assess how well each integration solution aligns with your infrastructure. iPaaS is typically easier to implement and integrates well with cloud-based applications, while ESB excels in integrating legacy systems and supporting diverse protocols.
Team skillset and expertise: Evaluate your team’s skillset and expertise in integration technologies. iPaaS solutions often have user-friendly interfaces and require less coding, making them accessible to business users. ESB implementations, on the other hand, may require more technical expertise and experience in integration development.
Case studies
Company A: Startup with cloud-based applications
Company A, a rapidly growing startup, relies on multiple cloud-based applications for different business functions. Their integration requirements involve synchronizing customer data, automating order processing, and connecting marketing systems. In this scenario, iPaaS would be a suitable choice for Company A due to its simplicity, scalability, and ability to integrate cloud applications efficiently.
Company B: Established enterprise with legacy systems
Company B, an established enterprise with a mix of legacy and modern applications, needs to integrate its ERP, CRM, and supply chain systems. Additionally, they require B2B integration with suppliers and partners. Considering the complexity and the need for legacy system integration, ESB would be a better fit for Company B as it provides robust message routing, protocol mediation, and legacy system integration capabilities.
Company C: Growing e-commerce business
Company C is an e-commerce business experiencing rapid growth. They need to integrate their e-commerce platform with inventory management systems, payment gateways, and shipping providers. In this case, a hybrid approach combining iPaaS and ESB would be beneficial. iPaaS can handle cloud-based integrations, while ESB can facilitate the integration with external systems and legacy infrastructure.
Hybrid approach: Combining iPaaS and ESB
For organizations with diverse integration needs, a hybrid approach can be adopted, combining the strengths of both iPaaS and ESB. Hybrid integration platforms allow businesses to leverage iPaaS for cloud-based integrations while using ESB to handle complex on-premises integrations and legacy system connectivity. This approach offers flexibility, scalability, and the ability to address diverse integration scenarios.
Conclusion
Choosing the right integration solution for your business is crucial to ensure seamless data flow, optimize business processes, and drive innovation. iPaaS and ESB offer distinct features and benefits, catering to different integration requirements and organizational contexts. Evaluate your integration needs, consider factors such as scalability, budget, and team expertise, and explore use cases and case studies to make an informed decision. Additionally, a hybrid approach combining iPaaS and ESB can provide a comprehensive solution that meets your organization’s unique integration challenges. Remember, a well-planned integration strategy is key to achieving digital transformation and staying competitive in today’s fast-paced business landscape.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!