The interconnectedness of the digital landscape has paved the way for seamless communication and data flow among applications, systems, and services. At the core of this interconnected world lies integration, the fundamental force that enables efficient connectivity. However, integration has come a long way from its humble beginnings as point-to-point solutions. It has evolved into a sophisticated hybrid approach that empowers businesses to operate in a new manner.
To truly appreciate the significance of integration in our interconnected world, it is crucial to delve into its evolution, tracing its origins and the transformative impact it has had across diverse industries.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!
Inception: The Advent of Point-to-Point Integration
Integration, in its earliest form, emerged with the need to connect isolated systems and enable data exchange. Point-to-point integration, born in the nascent stages of technological progress, involved creating direct connections between individual systems. While effective for limited-scale integrations, this approach quickly revealed its shortcomings as organizations sought to interconnect an ever-growing network of applications and systems.
The Limitations of Point-to-Point Integration
As organizations expanded their digital footprint, the limitations of point-to-point integration became increasingly apparent.
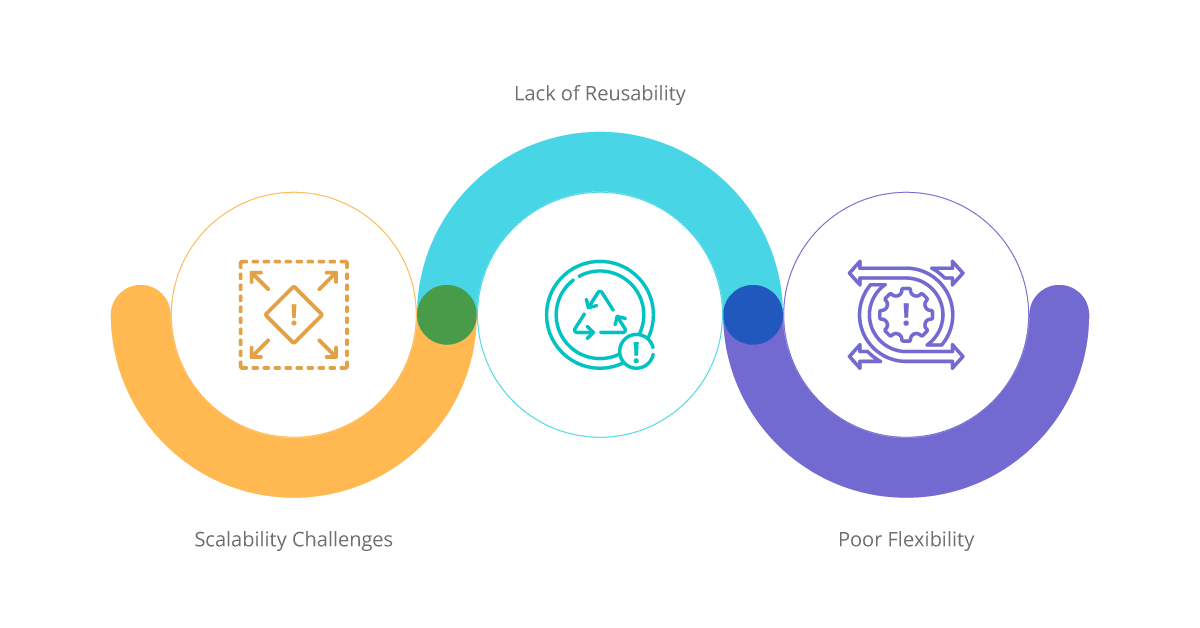
Scalability Challenges: With each new system added to the network, the complexity of managing and maintaining individual connections grew exponentially. As a result, organizations found themselves grappling with a convoluted web of integrations that hindered scalability and efficiency. For example, a company with ten applications might require 45 individual connections, and this number increases to 495 connections with twenty applications.
Lack of Reusability: Point-to-point integration relied on custom-built connections, leading to redundant efforts and increased development time. The absence of reusable integration components impeded agility, innovation, and the ability to respond swiftly to evolving business needs. For instance, when a new application needed to be integrated into the existing ecosystem, developers had to start from scratch, duplicating efforts and delaying time-to-market.
Poor Flexibility: Making changes or incorporating new systems in a point-to-point model necessitated modifying all existing connections. This lack of flexibility incurred high maintenance costs hindered adaptability and impeded organizations from embracing emerging technologies. Additionally, modifying connections between multiple systems often resulted in system downtime, disrupting crucial business operations.
Middleware and the Rise of Enterprise Service Bus (ESB)
Recognizing the limitations of point-to-point integration, the industry embraced middleware solutions as a means to centralize and streamline integrations.
Bridging the Gap: Middleware’s Role
Middleware emerged as a critical component in integration, acting as a central hub that facilitated communication and data exchange between disparate applications. It provided a standardized interface, abstracting the complexities of individual system integrations. Middleware solutions encompassed various technologies such as message queues, message brokers, and application servers.
Middleware allowed organizations to establish a hub-and-spoke model, where multiple applications are connected to a central middleware layer. Instead of creating numerous point-to-point connections, applications communicate with the middleware, which handled the routing of messages to the appropriate destinations. This approach significantly reduced the complexity of managing integrations.
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB): Orchestrating Integration
Building upon the middleware concept, Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) emerged as a comprehensive integration platform. ESBs facilitated intelligent routing, message transformation, and mediation, enabling seamless integration across multiple applications and systems. ESBs served as a middleware infrastructure that supported a broader range of integration patterns and capabilities.
ESBs introduced additional features to enhance integration capabilities, such as:
Message Transformation: ESBs allowed the transformation of messages between different formats, protocols, and data structures, ensuring compatibility and consistency across integrated systems. For example, a message received in XML format could be transformed into JSON format before being delivered to the destination system.
Protocol Translation: ESBs acted as intermediaries between systems using different communication protocols, translating messages from one protocol to another. This capability enabled seamless integration between systems that spoke different “languages.” For instance, an ESB could enable communication between a system using the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) and another system using Representational State Transfer (REST).
Event-Driven Architecture: ESBs embraced event-driven integration, allowing systems to react to specific events or triggers. This approach enabled real-time data exchange and facilitated the coordination of complex business processes across multiple systems.
The Era of Hybrid Integration: Adapting to a Complex Digital Landscape
The advent of cloud computing, mobile applications, and the Internet of Things (IoT) ushered in a new era of integration complexities, necessitating the emergence of hybrid integration approaches.
Hybrid Integration Platforms (HIP): Bridging the Divide
Hybrid Integration Platforms (HIPs) arose as a response to the growing demand for flexibility, scalability, and agility. HIPs combine the strengths of on-premises and cloud-based integration solutions, providing a unified platform to manage integrations across diverse environments.
HIPs encompass a comprehensive set of tools, technologies, and services that facilitate hybrid integration. Key components of HIPs include:
On-Premises Integration: HIPs allow organizations to connect and integrate their existing on-premises applications, databases, and systems. This capability is crucial for industries that have sensitive data or compliance requirements that necessitate on-premises infrastructure.
Cloud Integration: HIPs provide connectors and adapters to integrate with a wide range of cloud-based applications and services. This capability enables organizations to leverage the scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of cloud computing.
API Management: HIPs offer robust API management capabilities, allowing organizations to expose and manage APIs securely. This feature enables seamless integration with external partners, fosters collaboration, and opens up new revenue streams through API monetization.
Data Transformation and Mapping: HIPs provide visual data mapping tools that simplify the process of transforming data between different formats and structures. This capability ensures compatibility and consistency across integrated systems, reducing development time and effort.
Workflow Orchestration: HIPs enable the design and orchestration of complex integration workflows and business processes. Organizations can automate data flows, trigger actions based on specific events, and implement sophisticated business logic to streamline operations.
Monitoring and Management: HIPs offer comprehensive monitoring and management capabilities, providing visibility into integration performance, error handling, and overall system health. Real-time monitoring dashboards, alerting mechanisms, and logging functionalities help organizations proactively identify and address integration issues.
Realizing the Advantages of Hybrid Integration
Hybrid integration offers a myriad of advantages over traditional approaches, including:
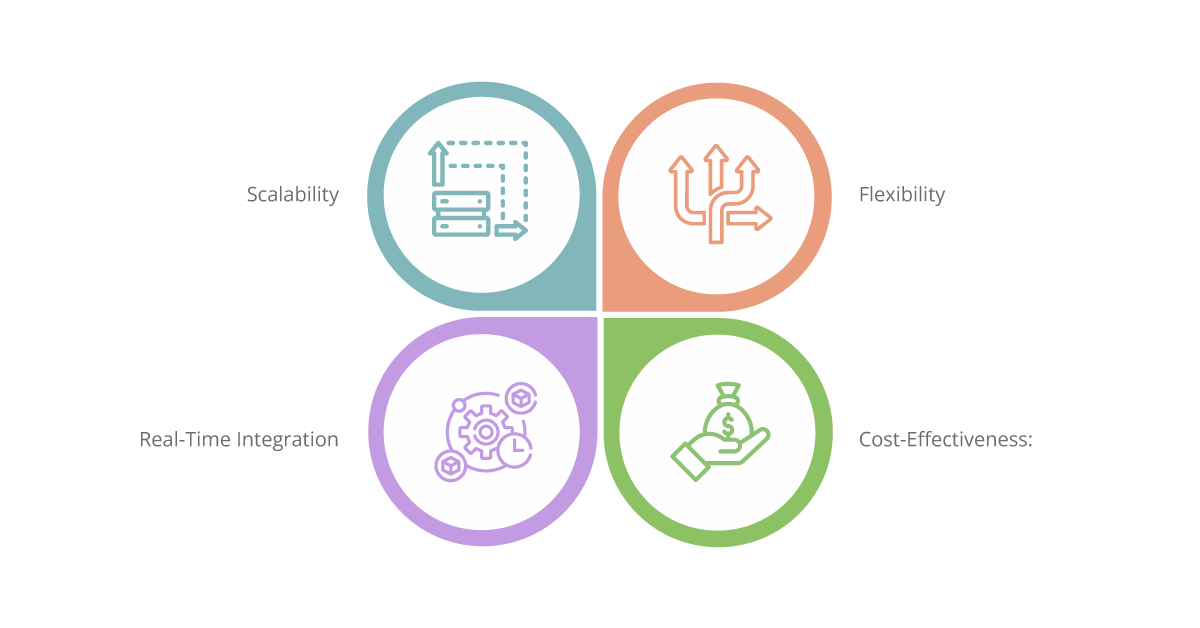
Scalability: One of the significant benefits of hybrid integration is its ability to handle scalability effortlessly. With the dynamic provision of cloud-based integration components, organizations can rapidly scale their integration infrastructure to meet growing data demands. This scalability ensures that businesses can handle increased data volume without compromising performance or incurring excessive costs. Whether it’s a sudden surge in customer transactions or a spike in data volume due to seasonal variations, hybrid integration platforms (HIPs) provide the necessary scalability to keep operations running smoothly.
Flexibility: Flexibility is a key characteristic of hybrid integration. By seamlessly connecting cloud-based applications, on-premises systems, and external partners, organizations can adapt to changing business requirements more effectively. The flexibility of hybrid integration enables businesses to adopt new technologies, integrate with third-party services, and explore innovative solutions. It empowers organizations to respond swiftly to market changes, customer demands, and industry trends. With hybrid integration, businesses have the agility to embrace digital transformation initiatives, experiment with new ideas, and stay ahead of the competition.
Cost-Effectiveness: Cost-effectiveness is a critical factor in any business decision, and hybrid integration excels in this aspect. By leveraging pre-built connectors, reusable integration components, and cloud-based resources, organizations can significantly reduce development and maintenance costs. The centralized management and monitoring capabilities provided by HIPs streamline operations, improve efficiency, and drive cost savings. With hybrid integration, businesses can achieve their integration goals without incurring excessive expenses, making it a cost-effective solution for enterprises of all sizes.
Real-Time Integration: Real-time integration is a game-changer in today’s fast-paced business environment. HIPs enable organizations to achieve real-time data synchronization and event-driven integrations, providing up-to-date insights for improved operational efficiency and timely decision-making. Real-time integration ensures that businesses have access to the most recent and accurate data, enabling them to respond quickly to changing market conditions, customer needs, and emerging opportunities. It empowers organizations to implement real-time analytics, generate instant reports, and automate processes for better productivity and enhanced customer experiences.
Aonflow is the leading integration platform.
You can kick-start by integrating your first-ever workflow in just a matter of minutes.
Real-World Use Cases: Transforming Industries with Hybrid Integration
To truly grasp the transformative power of hybrid integration, let’s explore real-world use cases across industries:
Healthcare Industry: The healthcare industry relies heavily on the secure and seamless exchange of patient data across various systems and applications. Hybrid integration facilitates interoperability between electronic health record (EHR) systems, medical devices, telemedicine platforms, and healthcare applications. For example, a hybrid integration solution can enable the seamless sharing of patient data between a hospital’s EHR system and a telehealth application. This integration ensures accurate and timely diagnoses, improves patient care coordination, and enhances overall healthcare delivery.
E-commerce and Supply Chain: In the e-commerce and supply chain sector, effective integration is crucial for streamlined operations and a seamless customer experience. Hybrid integration enables organizations to synchronize inventory, orders, and customer data across various platforms, ensuring accurate stock levels, reducing fulfillment time, and optimizing the overall supply chain. By connecting an e-commerce website with inventory management systems, order fulfillment systems, and shipping providers, a hybrid integration platform enables real-time inventory updates, automated order processing, and end-to-end visibility for customers. This integration enhances efficiency, minimizes errors, and delights customers with faster order fulfillment and delivery.
Financial Services: Hybrid integration plays a vital role in the financial services industry, where secure and reliable data exchange is essential for banking operations, payment processing, and personalized customer experiences. By connecting core banking systems, payment gateways, CRM platforms, and third-party financial services, hybrid integration enables secure transactions, seamless payment processing, and personalized financial recommendations. For instance, a hybrid integration solution can facilitate real-time payment processing, instant fund transfers between accounts, and personalized financial advice based on customer data. This integration ensures data integrity, enhances operational efficiency, and delivers a seamless banking experience to customers.
Manufacturing Industry: In the manufacturing sector, hybrid integration plays a pivotal role in streamlining operations, optimizing supply chain management, and enhancing collaboration with suppliers and partners. By integrating enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, inventory management systems, production control systems, and supplier systems, organizations can achieve end-to-end visibility and control over their manufacturing processes. For example, a hybrid integration solution can enable real-time data exchange between a manufacturer’s ERP system and its suppliers’ systems, facilitating seamless order placement, inventory management, and production scheduling. This integration ensures accurate demand forecasting, reduces lead times, and enhances supply chain efficiency, resulting in improved productivity and cost savings.
Hospitality and Travel Industry: In the hospitality and travel industry, where customer satisfaction is paramount, hybrid integration plays a crucial role in providing personalized experiences and seamless booking processes. By integrating customer relationship management (CRM) systems, reservation systems, property management systems, and online booking platforms, organizations can deliver tailored services to their guests and streamline booking operations. For instance, a hybrid integration platform can enable real-time synchronization of customer data, allowing hotels and travel agencies to offer personalized recommendations, loyalty rewards, and seamless booking experiences across various channels. This integration enhances customer satisfaction, improves operational efficiency, and drives revenue growth.
Education Sector: The education sector has also embraced hybrid integration to enhance student experiences, streamline administrative processes, and improve data management. By integrating student information systems, learning management systems, financial systems, and communication platforms, educational institutions can provide a cohesive and personalized learning environment for students. For example, a hybrid integration solution can enable seamless data synchronization between an institution’s student information system and its learning management system, ensuring accurate enrollment, grade tracking, and course management. This integration enhances administrative efficiency, facilitates effective communication between stakeholders, and improves student outcomes.
Retail Industry: The retail industry heavily relies on efficient integration to provide a seamless shopping experience across multiple channels, manage inventory, and streamline supply chain operations. Hybrid integration enables retailers to connect their e-commerce platforms, point-of-sale systems, inventory management systems, and customer relationship management systems. By integrating these systems, retailers can achieve real-time inventory visibility, enable omnichannel capabilities such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), and deliver personalized shopping experiences. For example, a hybrid integration solution can synchronize inventory levels across online and offline channels, allowing customers to check product availability in real-time and make informed purchasing decisions. This integration enhances operational efficiency, reduces stockouts, and improves customer satisfaction.
Energy and Utilities Sector: In the energy and utilities sector, effective integration is crucial for managing complex infrastructure, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring reliable service delivery. Hybrid integration enables the integration of systems such as energy management systems, metering systems, asset management systems, and customer engagement platforms. By integrating these systems, energy and utility companies can monitor energy usage in real-time, optimize distribution networks, and provide personalized energy usage insights to customers. For instance, a hybrid integration solution can enable the seamless exchange of data between smart meters, energy management systems, and billing systems, allowing customers to monitor their energy consumption, receive accurate bills, and make informed decisions to reduce energy usage. This integration enhances operational efficiency, promotes sustainability, and improves customer satisfaction.
Automotive Industry: The automotive industry leverages hybrid integration to optimize manufacturing processes, enhance vehicle connectivity, and deliver innovative mobility services. By integrating systems such as product lifecycle management (PLM) systems, manufacturing execution systems (MES), vehicle telemetry systems, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems, automotive companies can achieve end-to-end visibility and control over their production and customer lifecycle. For example, a hybrid integration solution can enable real-time data exchange between manufacturing systems and vehicle telemetry systems, enabling proactive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and over-the-air software updates for vehicles. This integration enhances production efficiency, enables connected car features, and improves the overall customer experience.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Hybrid Integration
The evolution of integration from point-to-point to hybrid approaches has revolutionized the way businesses connect their systems and applications. Middleware solutions and the rise of Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) introduced centralized integration hubs and orchestration capabilities, addressing the limitations of point-to-point integration. Hybrid Integration Platforms (HIPs) emerged further revolutionizing integration by combining the strengths of on-premises and cloud-based solutions, enabling scalability, flexibility, and real-time data flow across diverse environments.
Understanding the historical context and embracing the latest integration methodologies empowers organizations to optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation in an ever-changing digital landscape. Hybrid integration offers scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and real-time capabilities that businesses need to thrive in the interconnected world. By embracing the power of hybrid integration, organizations position themselves at the forefront of progress, ready to seize opportunities, overcome challenges, and achieve success in the dynamic digital era.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!