As enterprise adoption of cloud-based applications gains momentum globally and in Asia, IT teams find themselves navigating the complexities of integrating new technology with existing legacy systems. This challenge, often termed hybrid IT, underscores the importance of seamless integration in the modern IT landscape. In this blog post, we delve into the significance of iPaaS in streamlining application integration and addressing the needs of diverse clients across industries.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!
Understanding the Landscape
Organizations are increasingly embracing Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications alongside on-premises systems. While the benefits of cloud and SaaS solutions are evident – offering agility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness – the integration of these solutions with legacy systems poses a significant challenge.
In the landscape of IT environments, the integration of applications has become a crucial aspect for organizations aiming to stay competitive and efficient. iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) emerges as a powerful solution to streamline this integration process, offering numerous benefits to businesses across industries. Let’s explore how iPaaS simplifies application integration and who stands to benefit from its implementation.
Understanding Application Integration in IT Environments
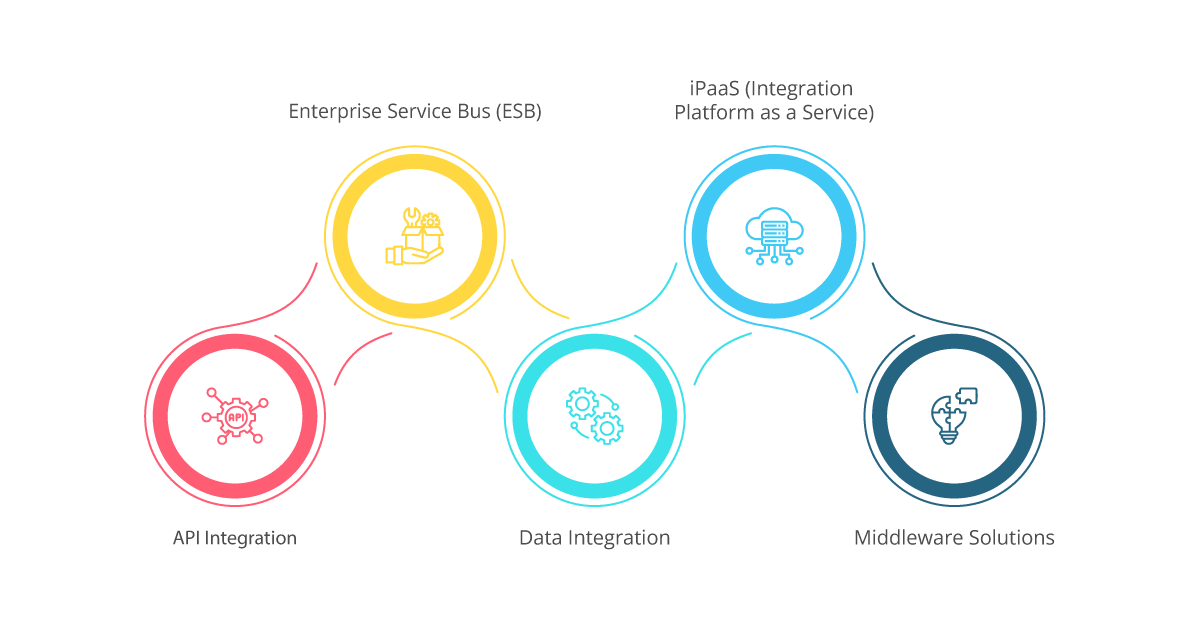
Application integration in IT environments refers to the process of connecting different software applications and systems to work together seamlessly. This integration is essential for modern organizations to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance overall productivity. Several key strategies and technologies are employed to achieve effective application integration:
API Integration:
Definition: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) provide a standardized way for different software components to communicate and interact with each other. API integration involves leveraging these interfaces to enable data exchange and functionality sharing between applications.
Example: A social media management platform integrates with various social media APIs (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, Instagram) to enable users to manage multiple social accounts from a single dashboard, schedule posts, and analyze engagement metrics.
Enterprise Service Bus (ESB):
Definition: ESB is a software architecture model used for integrating various applications and services within an enterprise. It acts as a centralized hub that facilitates communication, message routing, and transformation between different systems.
Example: In a banking environment, an ESB connects core banking systems with online banking platforms, ATM networks, and mobile banking applications. It ensures smooth transaction processing, account management, and customer authentication across all channels.
Data Integration:
Definition: Data integration involves combining data from disparate sources, formats, and locations into a unified view. This enables organizations to gain insights, make informed decisions, and improve business processes.
Example: A retail chain integrates data from point-of-sale (POS) systems, inventory databases, and customer relationship management (CRM) platforms to create a comprehensive view of sales performance, inventory levels, and customer preferences. This integrated data can be used for inventory optimization, targeted marketing campaigns, and personalized customer experiences.
iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service):
Definition: iPaaS is a cloud-based platform that provides tools and services for integrating applications, data, and processes across different cloud environments and on-premises systems. It offers features such as pre-built connectors, drag-and-drop interfaces, and scalability.
Example: A healthcare organization adopts iPaaS to integrate electronic health records (EHR) systems, medical billing software, and patient scheduling applications. iPaaS allows seamless data exchange between these systems while ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA.
Middleware Solutions:
Definition: Middleware refers to software components that facilitate communication and data exchange between disparate applications and systems. Middleware solutions often include message brokers, adapters, and integration frameworks.
Example: An e-commerce company uses middleware solutions to connect its online storefront with back-end systems such as inventory management, order processing, and shipping logistics. Middleware handles data transformation, transaction management, and error handling to ensure the smooth operation of the entire e-commerce ecosystem.
Effective application integration in IT environments requires careful planning, robust architecture, and ongoing maintenance to adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements. By seamlessly connecting disparate applications and systems, organizations can unlock new opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and growth.
The Challenges of Application Integration in IT Environments
Application integration in IT environments presents several challenges that organizations must address to ensure seamless operation and optimal performance. These challenges arise due to the complexity of modern IT infrastructures, diverse software applications, and evolving business requirements. Some of the key challenges include:
Diverse Application Ecosystems:
Issue: Organizations often use a mix of legacy systems, commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) software, custom-developed applications, and cloud-based services. Integrating these diverse application ecosystems requires overcoming compatibility issues, data format mismatches, and varying communication protocols.
Example: A manufacturing company may have legacy production management systems running on-premises while using cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) software and third-party logistics (3PL) applications. Integrating these disparate systems to streamline order processing and inventory management poses a significant challenge.
Data Silos and Fragmentation:
Issue: Data silos occur when information is isolated within specific applications or departments, making it difficult to access and share across the organization. Fragmented data leads to inefficiencies, duplication of effort, and inconsistencies in decision-making.
Example: In a healthcare setting, patient data may be stored in separate electronic health record (EHR) systems, laboratory information systems (LIS), and billing software. Without effective integration, healthcare providers may struggle to access comprehensive patient records, leading to delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Complexity of Integration Technologies:
Issue: Integration technologies such as APIs, enterprise service buses (ESBs), middleware solutions, and iPaaS offer various capabilities and features. Choosing the right technology stack and implementing integration solutions require specialized skills and expertise.
Example: A financial institution aiming to modernize its banking infrastructure must evaluate different integration approaches to connect core banking systems with mobile banking apps, payment gateways, and third-party financial services. Selecting and configuring the most suitable integration technologies can be challenging without proper understanding and experience.
Security and Compliance Concerns:
Issue: Integrating applications involves exchanging sensitive data and exposing interfaces for communication, which introduces security risks such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance violations. Ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and regulatory compliance is essential for protecting sensitive information.
Example: A government agency integrating systems for citizen services must adhere to strict data protection regulations and privacy laws. Implementing encryption, access controls, and audit trails to safeguard citizen data against security threats and regulatory non-compliance is a critical challenge.
Scalability and Performance Optimization:
Issue: As organizations grow and evolve, the volume of data and transactions handled by integrated systems increases. Scalability and performance optimization become crucial to maintain responsiveness, reliability, and efficiency.
Example: A rapidly expanding e-commerce platform experiences spikes in website traffic during seasonal promotions or sales events. Scaling up backend systems such as inventory management, order processing, and payment processing to handle high transaction volumes without performance degradation presents a significant integration challenge.
Addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach encompassing strategic planning, architectural design, technology selection, governance frameworks, and continuous monitoring. By overcoming the obstacles to application integration, organizations can unlock the full potential of their IT environments, drive innovation, and achieve competitive advantage in the digital age.
Aonflow is the leading integration platform.
You can kick-start by integrating your first-ever workflow in just a matter of minutes.
How iPaaS Addresses Integration Challenges in IT Environments
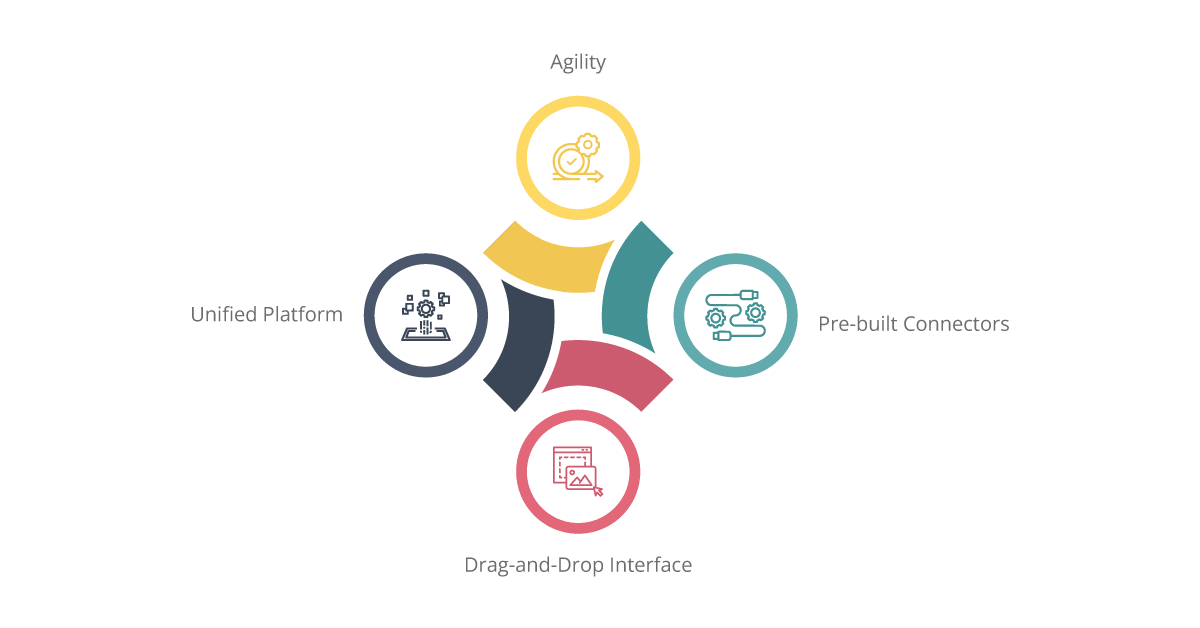
Unified Platform:
iPaaS provides a centralized platform for integrating various applications and data sources. This eliminates the need for multiple point-to-point integrations, reducing complexity and enhancing manageability.
Example: Instead of managing separate integrations for CRM, ERP, and HR systems, a company can use iPaaS to create a unified platform where data from all these systems is seamlessly integrated. For instance, customer information from the CRM can be synchronized with the ERP system for streamlined order processing.
Drag-and-Drop Interface:
Unlike traditional integration methods that require extensive coding, iPaaS offers a user-friendly interface with drag-and-drop functionality. This empowers non-technical users to create integration workflows quickly and efficiently.
Example: A marketing team can use iPaaS to create an automated workflow that triggers email campaigns based on customer interactions with the company’s website. With a drag-and-drop interface, they can easily map out the flow of data from the website analytics tool to the email marketing platform without writing any code.
Pre-built Connectors:
iPaaS comes equipped with pre-built connectors for popular applications and services, enabling rapid integration without the need for custom development. This accelerates time-to-market and minimizes implementation costs.
Example: A retail business looking to integrate its online store with a popular payment gateway can leverage iPaaS with pre-built connectors. Instead of developing custom code to enable transactions, they can simply use the pre-built connector to facilitate secure payments, saving time and resources.
Agility:
With iPaaS, organizations can scale their integration efforts seamlessly as their business grows. The flexible nature of iPaaS allows for easy customization and adaptation to changing business requirements.
Example: A growing e-commerce company can start with basic integrations between its website, inventory management system, and shipping provider using iPaaS. As the company expands into new markets or adds more products, it can easily scale up its integration efforts by adding new connections or customizing existing workflows to meet evolving business needs.
Who Benefits from iPaaS Integration?
- Enterprise IT Departments: Large enterprises with complex IT infrastructures benefit from iPaaS by streamlining integration processes across departments and business units. iPaaS enables IT teams to manage integrations more efficiently, freeing up time and resources for strategic initiatives.
- SaaS Providers: Software-as-a-service (SaaS) providers leverage iPaaS to offer seamless integration capabilities to their customers. By integrating with iPaaS platforms, SaaS providers enhance the value proposition of their offerings and attract more customers.
- Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs): SMBs often lack the resources and expertise to develop custom integration solutions. iPaaS levels the playing field by providing affordable and accessible integration capabilities, allowing SMBs to compete with larger enterprises effectively.
- IT Consultants and Service Providers: IT consultants and service providers leverage iPaaS to deliver value-added services to their clients. iPaaS enables them to offer comprehensive integration solutions without the need for extensive development efforts, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Conclusion
iPaaS emerges as a game-changer in the realm of application integration, offering a simplified and scalable solution to complex integration challenges. Whether you’re a large enterprise, a SaaS provider, an SMB, or an IT service provider, iPaaS provides tangible benefits that drive efficiency, agility, and innovation in IT environments. Embrace iPaaS today and unlock the full potential of seamless application integration for your organization.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!