Healthcare integration has evolved tremendously with the advent of digital transformation. One of the key drivers of this evolution is Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS). This cloud-based solution offers a robust framework for connecting disparate systems, applications, and data sources, streamlining operations, and ensuring seamless data flow. But beyond the efficiency and operational improvements, iPaaS brings significant security benefits to the healthcare sector, which is critical given the sensitive nature of health data.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!
iPaaS in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is undergoing a digital transformation, driven by the need for improved patient care, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) is playing a pivotal role in this transformation by providing the tools and frameworks needed to connect disparate healthcare systems and data sources seamlessly. Here, we explore how iPaaS is being utilized in healthcare, its importance, and the benefits it brings to the sector.
The Role of iPaaS in Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, data is generated from various sources, including electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory information systems (LIS), radiology information systems (RIS), billing systems, and patient management applications. Managing this data effectively and ensuring it is available where and when it is needed is critical for providing high-quality patient care. iPaaS solutions facilitate this by enabling the integration of diverse systems and data sources, ensuring seamless data flow across the healthcare ecosystem.
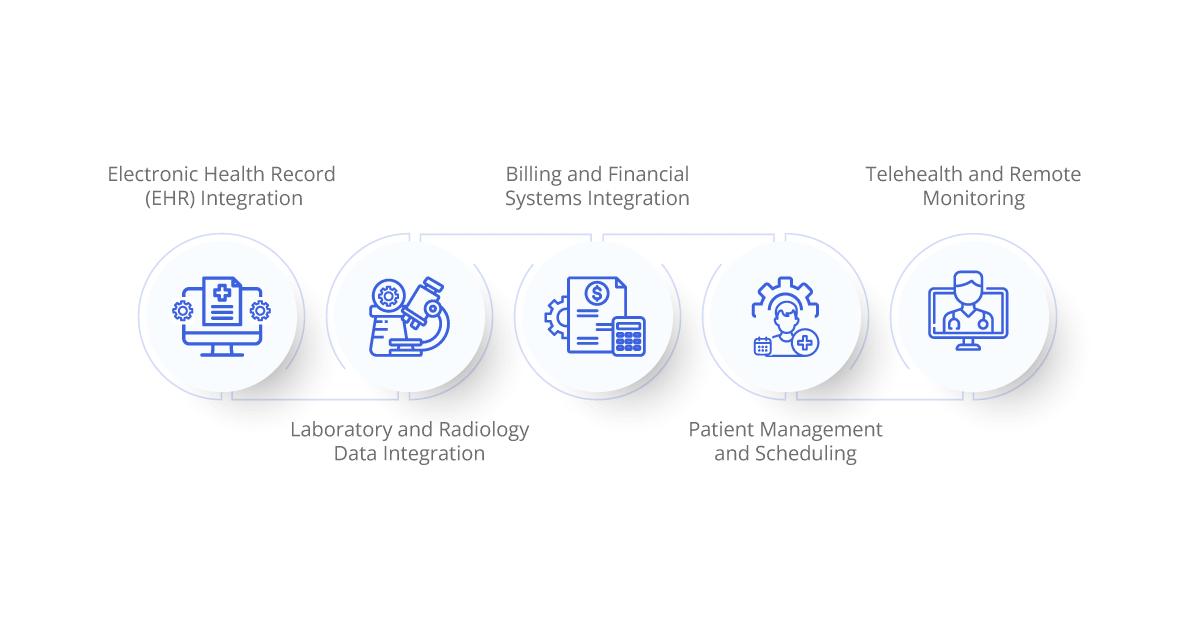
Key Applications of iPaaS in Healthcare
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) Integration: EHRs are central to modern healthcare, providing a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history. iPaaS platforms enable the integration of EHRs with other healthcare systems, ensuring that patient data is accessible across different departments and facilities. This integration is crucial for providing coordinated and continuous care.
- Laboratory and Radiology Data Integration: Laboratories and radiology departments generate a significant amount of data that needs to be integrated with patient records. iPaaS platforms help in seamlessly integrating laboratory and radiology information systems with EHRs, ensuring that test results and imaging data are readily available to healthcare providers.
- Billing and Financial Systems Integration: Accurate billing and efficient financial management are essential for the sustainability of healthcare providers. iPaaS solutions integrate billing systems with clinical systems, ensuring that billing data is accurate and up-to-date. This integration reduces administrative burdens and helps in minimizing billing errors.
- Patient Management and Scheduling: Patient management and scheduling systems are critical for managing appointments, admissions, and discharges. iPaaS platforms enable the integration of these systems with EHRs and other clinical systems, ensuring that patient schedules are managed efficiently and that all relevant information is available to healthcare providers.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring: The rise of telehealth and remote patient monitoring has added new dimensions to healthcare delivery. iPaaS solutions facilitate the integration of telehealth platforms and remote monitoring devices with EHRs, ensuring that data from remote consultations and monitoring devices is seamlessly integrated into the patient’s health record.
Benefits of iPaaS in Healthcare Integration
Enhanced Data Accessibility and Patient Care
By integrating various healthcare systems, iPaaS ensures that healthcare providers have access to a comprehensive and up-to-date view of a patient’s medical history. This holistic view is essential for making accurate diagnoses, developing effective treatment plans, and providing personalized care. For example, a physician can quickly access a patient’s lab results, imaging data, and previous treatment records, enabling more informed decision-making.
Operational Efficiency
iPaaS platforms streamline healthcare operations by automating data exchange between systems. This automation reduces the need for manual data entry and minimizes the risk of errors, leading to more efficient workflows. For instance, patient information entered during an initial consultation can automatically populate relevant fields in the billing system, reducing administrative tasks and speeding up the billing process.
Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare organizations must comply with stringent regulations designed to protect patient data, such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe. iPaaS platforms help ensure compliance by providing built-in security features such as data encryption, access control, and audit trails. These features ensure that patient data is handled securely and that all data access and modifications are logged for audit purposes.
Improved Data Quality and Consistency
Data quality is critical in healthcare, where inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to misdiagnosis and ineffective treatments. iPaaS platforms provide tools for data validation and transformation, ensuring that data is consistent and accurate across all integrated systems. This improves the reliability of the data used for clinical decision-making and research.
Flexibility and Scalability
Healthcare organizations operate in a dynamic environment where new technologies, regulations, and patient needs continually emerge. iPaaS platforms offer the flexibility to quickly integrate new systems and applications, ensuring that healthcare providers can adapt to changes without significant disruption. Additionally, iPaaS solutions are scalable, allowing healthcare organizations to handle increasing data volumes and integration complexities as they grow.
Importance of Integration in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations manage vast amounts of sensitive data, ranging from patient records to clinical research information. The integration of these disparate data sources is crucial for several reasons:
Enhanced Patient Care
- Comprehensive Patient Records: Integrated systems consolidate patient information from various sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory results, imaging studies, and pharmacy data. This consolidation provides healthcare providers with a comprehensive view of a patient’s medical history, enabling more accurate and timely diagnosis.
- Improved Decision-Making: With access to complete patient data, clinicians can make better-informed decisions about treatment plans. For instance, knowing a patient’s allergy history or previous adverse reactions to medications can prevent harmful prescriptions and improve patient safety.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Integration facilitates personalized medicine by allowing providers to tailor treatment plans based on a holistic understanding of the patient’s history, genetic information, lifestyle factors, and other relevant data. This personalized approach can lead to better outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.
- Enhanced Coordination of Care: When multiple healthcare providers can access the same integrated data, it ensures that all parties involved in a patient’s care are on the same page. This coordination is vital for managing chronic diseases, where patients often see multiple specialists.
- Real-Time Access to Information: Integrated systems enable real-time access to patient data, which is crucial in emergencies where quick decision-making can be a matter of life and death. For example, emergency room doctors can immediately access a patient’s medical history, allergies, and current medications, facilitating prompt and accurate treatment.
Operational Efficiency
- Reduced Redundancies: Integration eliminates data silos and reduces redundancies by ensuring that information entered into one system is automatically available across all connected systems. This prevents the need for duplicate data entry and minimizes errors.
- Streamlined Workflows: Integrated systems streamline administrative workflows by automating routine tasks, such as scheduling, billing, and reporting. This automation frees up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care rather than paperwork.
- Resource Optimization: By providing a complete view of operations, integrated systems help in optimizing the use of resources, such as staffing, equipment, and facilities. For instance, an integrated scheduling system can better manage patient appointments, reducing wait times and improving the utilization of clinical resources.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Integration fosters better collaboration among healthcare teams by providing a unified platform for communication and data sharing. This collaborative environment leads to more efficient and effective patient care.
- Improved Data Analytics: Integrated systems facilitate advanced data analytics, enabling healthcare organizations to derive insights from large datasets. These insights can help in identifying trends, improving patient outcomes, and making informed strategic decisions.
Regulatory Compliance
- Adherence to Standards: Healthcare organizations must comply with various regulations and standards designed to protect patient data and ensure its privacy and security. Integrated systems help ensure that data handling practices meet the requirements of regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
- Automated Compliance Reporting: Integrated systems can automate the generation of compliance reports, ensuring that all regulatory requirements are met without manual intervention. This reduces the administrative burden on healthcare providers and minimizes the risk of non-compliance.
- Enhanced Data Security: Integration platforms often come with built-in security features, such as encryption, access control, and audit trails. These features help protect sensitive patient data from breaches and unauthorized access, ensuring compliance with data protection laws.
- Audit Trails: Integrated systems maintain detailed audit trails of all data access and modifications, providing a transparent record for compliance audits. This transparency is crucial for demonstrating adherence to regulatory standards and for investigating any potential data breaches.
- Data Governance: Integrated systems support robust data governance practices by ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date across all platforms. Good data governance is essential for maintaining the integrity of patient information and for meeting regulatory requirements.
Interoperability and Standardization
- Seamless Data Exchange: Integration ensures that different systems and applications can communicate with each other effectively. This interoperability is crucial for seamless data exchange between various healthcare providers, laboratories, pharmacies, and insurance companies.
- Standardization of Data: Integrated systems often enforce standardization of data formats and terminologies, which is essential for accurate data exchange and analysis. Standardized data allows for more effective use of clinical decision support systems and other advanced healthcare technologies.
- Support for Emerging Technologies: As new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), become more prevalent in healthcare, integrated systems provide the foundation for their effective implementation. These technologies rely on access to large, standardized datasets to function effectively.
- Facilitating Research and Development: Integrated systems enable the aggregation of large datasets, which can be used for clinical research and the development of new treatments. Researchers can access comprehensive patient data, leading to more robust studies and faster advancements in medical knowledge.
Aonflow is the leading integration platform.
You can kick-start by integrating your first-ever workflow in just a matter of minutes.
Security Challenges in Healthcare Integration
Data Breaches and Cyber Attacks
Healthcare data is a prime target for cybercriminals due to its sensitive nature and high value on the black market. Data breaches can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and even endanger patient lives by disrupting critical services.
Compliance and Regulations
Healthcare providers must comply with stringent regulations designed to protect patient data. These include the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties and loss of reputation.
Interoperability Issues
Integrating different systems and applications poses significant challenges, particularly when dealing with legacy systems and disparate data formats. Ensuring secure and seamless data exchange while maintaining data integrity is a complex task.
How iPaaS Enhances Security in Healthcare Integration
In the realm of healthcare, where the protection of sensitive patient data is paramount, iPaaS plays a pivotal role in fortifying security measures. Let’s delve deeper into how iPaaS bolsters security in healthcare integration:
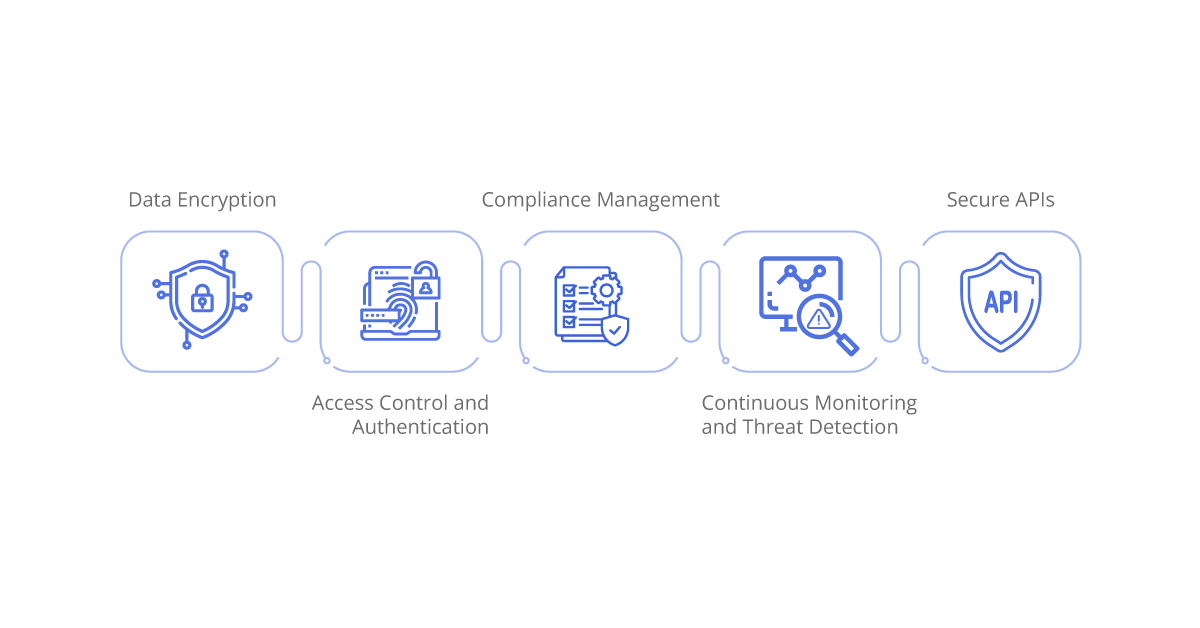
Data Encryption
- Protecting Data at Rest and in Transit: iPaaS platforms employ sophisticated encryption techniques to safeguard data both when it’s stored and during its transmission between systems. This ensures that even if intercepted, the data remains indecipherable and tamper-proof.
- Encryption at Rest: By converting stored data into an unreadable format, encryption at rest shields it from unauthorized access or theft.
- Encryption in Transit: Data is encrypted as it traverses between systems, thwarting any attempts at interception or eavesdropping during transfer.
Access Control and Authentication
- Ensuring Authorized Access: iPaaS platforms implement robust access control mechanisms to restrict access to sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized users can retrieve or manipulate it.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Permissions are assigned based on predefined user roles, limiting access to specific datasets or functionalities according to each user’s responsibilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of security, MFA mandates users to verify their identity through multiple authentication methods, such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens.
Compliance Management
- Facilitating Regulatory Compliance: iPaaS platforms are equipped with built-in features to assist healthcare organizations in adhering to regulatory requirements, safeguarding patient data, and ensuring compliance with laws such as HIPAA and GDPR.
- Audit Trails: Every access and data modification is automatically logged, creating a transparent record that can be audited to demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards.
- Data Masking: Sensitive data elements are concealed to protect patient information while still allowing it to be utilized for analysis and testing purposes, ensuring privacy and compliance.
Secure APIs
- Protecting Data Exchange: APIs are pivotal for seamless data exchange between systems, and iPaaS platforms ensure their security to safeguard against unauthorized access or manipulation of data.
- API Gateways: Acting as intermediaries, API gateways control and secure the traffic between systems, ensuring that only authenticated and authorized requests are processed.
- API Monitoring: iPaaS platforms continuously monitor API usage, tracking and analyzing traffic patterns to detect and respond to any suspicious activities in real time, mitigating potential security threats proactively.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
- Vigilant Surveillance: Advanced iPaaS platforms are equipped with continuous monitoring capabilities to detect and respond to security threats promptly.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS monitors network traffic for any signs of suspicious activity, immediately alerting administrators to potential security breaches.
- Behavioral Analytics: By analyzing user behavior patterns, behavioral analytics can identify anomalies that may indicate a security breach, enabling swift remedial action to be taken.
In a healthcare landscape where data privacy and security are paramount, iPaaS stands as a stalwart guardian, fortifying integration processes with robust encryption, stringent access controls, regulatory compliance measures, and vigilant threat detection mechanisms. By implementing iPaaS solutions, healthcare organizations can rest assured that their sensitive data remains protected against evolving cyber threats, ensuring the safety and confidentiality of patient information.
Best Practices for Implementing iPaaS in Healthcare
Conduct a Thorough Risk Assessment
Before implementing an iPaaS solution, healthcare organizations should conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential security vulnerabilities and determine the appropriate security measures.
Choose a Compliant iPaaS Provider
Select an iPaaS provider like Aonflow with a proven track record in healthcare integration and a commitment to regulatory compliance.
Ensure the provider offers features like data encryption, access control, and continuous monitoring.
Implement Strong Access Controls
Use role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to limit access to sensitive data and ensure that only authorized personnel can access critical systems.
Monitor and Update Regularly
Continuous monitoring is essential to detect and respond to security threats in real time. Regularly update the iPaaS platform to address any vulnerabilities and ensure the latest security features are in place.
Train Staff on Security Protocols
Educate healthcare staff on the importance of data security and provide training on how to use the iPaaS platform securely. This includes recognizing phishing attempts and other common cyber threats.
Future Trends in iPaaS and Healthcare Security
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are poised to enhance iPaaS platforms by providing advanced threat detection and predictive analytics. These technologies can help identify potential security breaches before they occur and automate responses to minimize damage.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain offers a secure, decentralized way to manage healthcare data. By integrating blockchain with iPaaS, healthcare organizations can ensure data integrity and transparency while protecting against unauthorized access.
Enhanced Privacy Measures
Future iPaaS platforms will likely incorporate more advanced privacy features, such as differential privacy and homomorphic encryption, to provide even greater protection for patient data.
Conclusion
iPaaS plays a crucial role in the digital transformation of healthcare. Beyond streamlining operations and improving data management, iPaaS offers significant security benefits that are essential for protecting sensitive healthcare data.
By leveraging advanced encryption, robust access controls, compliance management, secure APIs, and continuous monitoring, iPaaS platforms help healthcare organizations safeguard patient information and maintain regulatory compliance. As technology continues to evolve, iPaaS will undoubtedly become an even more critical component of secure healthcare integration, ensuring that patient data remains protected in an increasingly connected world.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!