Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) and data warehousing are critical technologies in modern manufacturing analytics. These technologies have revolutionized the way manufacturers approach data integration, analysis, and decision-making processes. iPaaS serves as the backbone for seamless integration, bridging the gap between diverse systems, applications, and data sources.
On the other hand, data warehousing acts as the central repository, consolidating vast amounts of data for in-depth analysis and reporting. Together, iPaaS and data warehousing empower manufacturers to delve deeper into their operational data, unlocking valuable insights that drive informed decision-making and operational excellence.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!
Understanding iPaaS
iPaaS is a cloud-based integration solution that connects various software applications, systems, and data sources. It simplifies the integration process by providing a platform for developing, deploying, and managing integrations without requiring extensive coding.
Key Features of iPaaS
- Scalability: Easily scales to handle increasing data volumes and integration complexity.
- Flexibility: Supports diverse integration scenarios, including cloud-to-cloud, cloud-to-on-premises, and on-premises-to-on-premises integrations.
- Real-Time Processing: Enables real-time data processing and integration, ensuring up-to-date information.
- User-Friendly Interface: Often includes drag-and-drop tools and pre-built connectors to simplify the integration process.
The Role of Data Warehousing in Manufacturing
What is a Data Warehouse?
The pivotal role of data warehousing in the manufacturing sector cannot be overstated. At its essence, a data warehouse serves as the linchpin of information management, acting as a centralized reservoir that meticulously houses both structured and unstructured data originating from diverse sources within and beyond the manufacturing domain. This repository is meticulously designed and tailored specifically to facilitate seamless query and analysis processes, thereby laying the groundwork for robust business intelligence (BI) and advanced analytics endeavors.
Within the manufacturing context, where data streams often emanate from a plethora of sources ranging from Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to Supply Chain Management (SCM) software and beyond, the data warehouse emerges as the nucleus of data aggregation and consolidation. By harmonizing these disparate data streams within a singular repository, the data warehouse eradicates the presence of information silos, thereby affording decision-makers an encompassing view of the manufacturing landscape.
Furthermore, the data warehouse is not merely a passive storage facility; rather, it assumes an active role in facilitating analytical endeavors. Its architectural design is finely tuned to accommodate queries of varying complexities, ensuring that users can extract actionable insights with unparalleled efficiency. From generating performance reports to scrutinizing production metrics and beyond, the data warehouse emerges as the bedrock upon which informed decision-making processes are erected.
Crucially, the data warehouse transcends the temporal constraints of the present, extending its purview to encompass historical data storage. By archiving records of production metrics, inventory levels, customer orders, and other pertinent data points, the data warehouse affords manufacturers the capability to embark upon trend analysis and forecasting endeavors with unparalleled precision. Armed with this historical perspective, manufacturers can anticipate future trends, identify potential bottlenecks, and chart strategic pathways toward operational optimization.
However, the efficacy of the data warehouse hinges upon the foundation of data quality management. Within the confines of this repository, stringent measures are instituted to uphold the sanctity of data integrity. From data validation to cleansing and enrichment endeavors, every facet of data quality management is meticulously attended to, thereby engendering a culture of trust and reliability in the analytics ecosystem.
The Need for Integration in Manufacturing Analytics
Data warehousing, as the cornerstone of manufacturing analytics, boasts a multitude of key features meticulously crafted to cater to the intricate needs of modern enterprises. These features collectively empower manufacturers to harness the full potential of their data assets, driving informed decision-making, operational optimization, and competitive advantage in an ever-evolving marketplace.
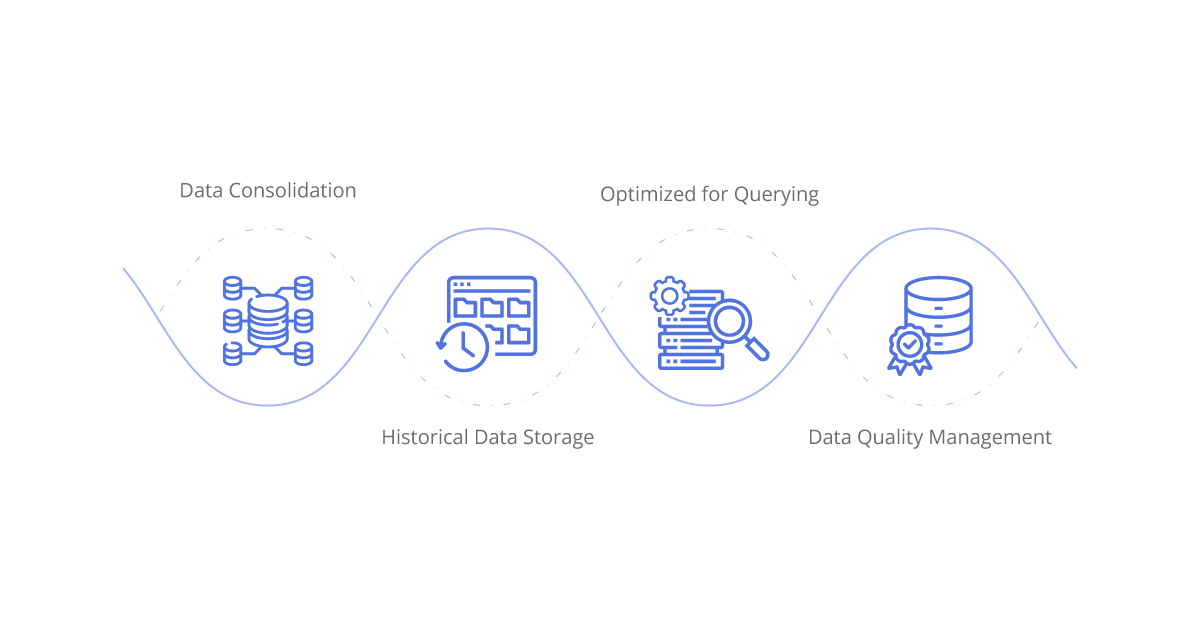
Data Consolidation:
At the heart of data warehousing lies the indispensable capability of data consolidation. This feature serves as the linchpin of information management, orchestrating the seamless aggregation of data streams emanating from a diverse array of sources. Whether it be data originating from Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Supply Chain Management (SCM) software, or beyond, the data warehouse serves as a centralized repository, harmonizing disparate data streams into a singular, coherent location.
By eradicating the presence of information silos and fostering a unified data ecosystem, data consolidation empowers decision-makers with an encompassing view of the manufacturing landscape, catalyzing the realization of actionable insights and informed decision-making processes.
Historical Data Storage:
In the realm of manufacturing analytics, the ability to glean insights from historical data assumes paramount importance. This necessitates the presence of robust historical data storage capabilities within the data warehouse.
By meticulously archiving records of production metrics, inventory levels, customer orders, and other pertinent data points, the data warehouse affords manufacturers the capability to embark upon trend analysis and forecasting endeavors with unparalleled precision. Armed with this historical perspective, decision-makers can discern patterns, anticipate future trends, and devise proactive strategies to navigate the complexities of the manufacturing landscape with confidence and foresight.
Optimized for Querying:
A hallmark feature of data warehousing is its architectural design finely tuned to accommodate queries of varying complexities. Structured in a manner that supports the execution of intricate queries and ad-hoc analysis, the data warehouse emerges as a veritable powerhouse of analytical capabilities.
Whether it be generating performance reports, scrutinizing production metrics, conducting root cause analysis, or exploring uncharted realms of data-driven insights, the data warehouse empowers users to extract actionable insights with unparalleled efficiency. This optimized querying capability ensures that decision-makers can navigate vast datasets with ease, expediting the process of information retrieval and engendering a culture of data-driven decision-making within the manufacturing ecosystem.
Data Quality Management:
In the realm of manufacturing analytics, the veracity of insights hinges upon the foundation of data quality management. Within the confines of the data warehouse, stringent measures are instituted to uphold the sanctity of data integrity. From data validation to cleansing and enrichment endeavors, every facet of data quality management is meticulously attended to, thereby engendering a culture of trust and reliability in the analytics ecosystem.
By ensuring data consistency, accuracy, and reliability, the data warehouse empowers decision-makers to place unwavering faith in the insights gleaned from their data assets, paving the way for informed decision-making processes and operational excellence.
Complex Manufacturing Environments
Manufacturing operations involve various systems, including Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), Supply Chain Management (SCM), and more. Each system generates valuable data that, when integrated, can provide comprehensive insights into manufacturing processes.
Data Silos and Fragmentation
Without integration, data remains siloed within individual systems, limiting the ability to perform holistic analysis. iPaaS and data warehousing break down these silos, enabling data consolidation and unified analytics.
Benefits of iPaaS and Data Warehousing Integration
Enhanced Decision-Making
Integrating iPaaS with data warehousing provides a holistic view of manufacturing operations, enabling data-driven decision-making. Real-time data integration ensures that decision-makers have access to the latest information.
Improved Operational Efficiency
By integrating disparate systems, manufacturers can automate workflows, reduce manual data entry, and minimize errors. This leads to increased efficiency and productivity.
Predictive Analytics and Maintenance
With consolidated data, manufacturers can leverage advanced analytics and machine learning to predict equipment failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and reduce downtime.
Supply Chain Optimization
Integrated data from SCM, ERP, and other systems allows for better supply chain visibility, helping manufacturers optimize inventory levels, reduce lead times, and improve demand forecasting.
Aonflow is the leading integration platform.
You can kick-start by integrating your first-ever workflow in just a matter of minutes.
Technical Aspects of iPaaS and Data Warehousing Integration
Data Integration Patterns
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
ETL is a traditional data integration pattern that involves extracting data from source systems, transforming it into a suitable format, and loading it into the data warehouse. iPaaS platforms often include ETL tools to streamline this process.
ELT (Extract, Load, Transform)
ELT is a variation where data is extracted and loaded into the data warehouse before transformation. This approach leverages the processing power of modern data warehouses for data transformation tasks.
Real-Time Data Integration
Real-time data integration enables continuous data flow between systems, providing up-to-date information for analytics and reporting. iPaaS supports real-time integration through APIs, webhooks, and streaming data technologies.
Data Quality and Governance
Ensuring data quality and governance is crucial for reliable analytics. iPaaS platforms like Aonflow often include features for data validation, cleansing, and enrichment. Data governance policies ensure data security, compliance, and consistent usage across the organization.
API Management
APIs are essential for connecting different systems and applications. iPaaS platforms provide API management capabilities, including API creation, monitoring, and security. This enables seamless communication between systems.
Scalability and Performance
Both iPaaS and data warehouses must handle large data volumes and complex queries efficiently. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability, allowing manufacturers to adjust resources based on demand. Performance optimization techniques, such as indexing and query optimization, ensure fast data retrieval and processing.
Security and Compliance
Manufacturing data often includes sensitive information that must be protected. iPaaS and data warehousing solutions implement robust security measures, including data encryption, access controls, and regular audits. Compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR and ISO, is also critical.
Use Cases of iPaaS and Data Warehousing in Manufacturing
Quality Control and Improvement
By integrating quality management systems (QMS) with MES and ERP data, manufacturers can analyze production quality in real-time, identify defects, and implement corrective actions promptly.
Inventory Management
Integration of inventory management systems with ERP and SCM data helps manufacturers maintain optimal inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize excess inventory.
Production Planning and Scheduling
Combining data from MES, ERP, and demand forecasting systems allows for more accurate production planning and scheduling, leading to better resource utilization and reduced lead times.
Customer Insights and Product Innovation
Integrating customer feedback and sales data with production data helps manufacturers understand customer preferences and drive product innovation. This can lead to improved customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
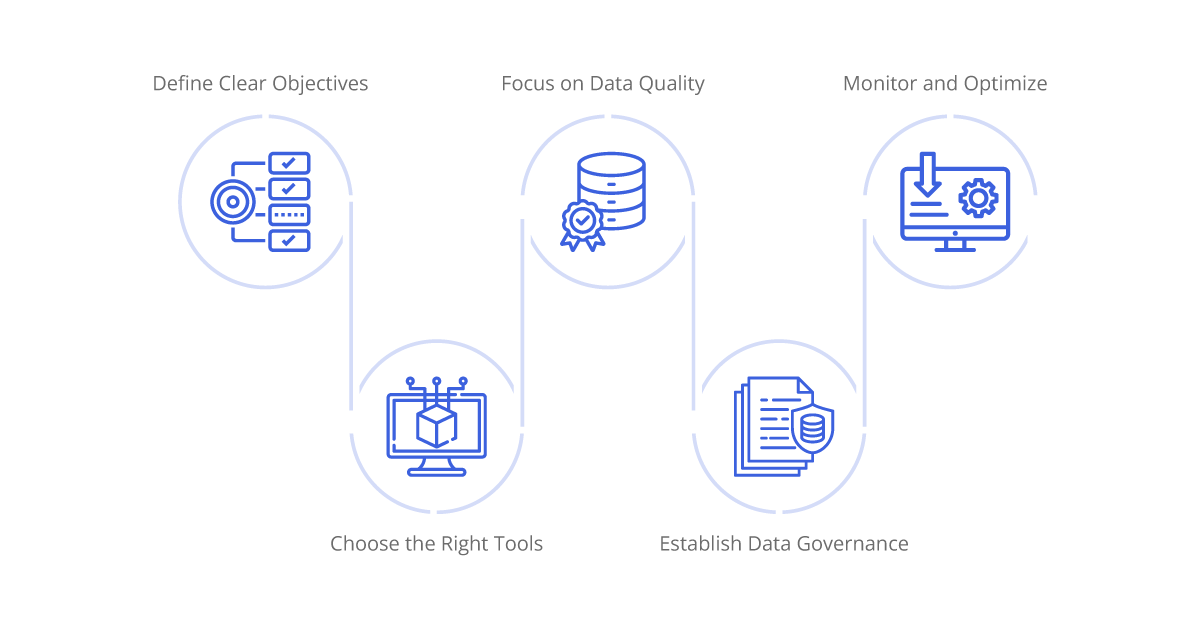
Define Clear Objectives
Clearly define the goals and objectives of the integration project. Understand what insights and outcomes you aim to achieve through data integration.
Choose the Right Tools
Select iPaaS and data warehousing solutions that align with your specific needs. Consider factors such as scalability, ease of use, integration capabilities, and cost.
Focus on Data Quality
Ensure that data is accurate, complete, and consistent. Implement data validation, cleansing, and enrichment processes to maintain high data quality.
Establish Data Governance
Develop and enforce data governance policies to manage data security, compliance, and usage. Define roles and responsibilities for data management.
Monitor and Optimize
Continuously monitor the performance of integration processes and optimize as needed. Use analytics and feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Future Trends in Manufacturing Analytics
Advanced Analytics and AI
The integration of iPaaS and data warehousing will continue to evolve, with advanced analytics and AI playing a significant role. Predictive and prescriptive analytics will become more prevalent, helping manufacturers make proactive decisions.
Edge Computing
Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source, will complement iPaaS and data warehousing. It enables real-time analytics and reduces latency, particularly for IoT and sensor data in manufacturing environments.
IoT and Sensor Integration
The proliferation of IoT devices and sensors in manufacturing will generate vast amounts of data. iPaaS will facilitate the integration of this data with existing systems, providing richer insights and enabling smarter manufacturing.
Enhanced Visualization and BI Tools
Visualization and BI tools will become more sophisticated, offering intuitive and interactive dashboards that provide actionable insights. These tools will be tightly integrated with data warehouses and iPaaS platforms.
Conclusion
iPaaS and data warehousing integration are transforming manufacturing analytics by providing a unified and comprehensive view of operations. The seamless flow of data between systems enables manufacturers to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and drive innovation. By leveraging the capabilities of iPaaS and data warehousing, manufacturers can stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world.
Integrating these technologies requires careful planning, a focus on data quality, and the right tools. As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of the latest trends and best practices will ensure that your integration efforts are successful and deliver tangible business value.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!