In today’s hyper-connected world, organizations rely on iPaaS to streamline their workflows and boost efficiency, seamlessly connecting apps, systems, and data. iPaaS is like the digital glue that holds everything together, making sure information flows smoothly across platforms. But with all this easy connectivity comes a new challenge: security. How do you protect sensitive data when everything is linked in the cloud?
This article dives into the top best practices to secure your iPaaS environment, helping you keep your data safe while enjoying the benefits of a fully integrated digital ecosystem.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!
Let’s Understand Security Threats

Before diving into best practices, it’s essential to grasp the security threats specific to iPaaS. These platforms tend to be targeted because they act as hubs, connecting critical data across multiple systems and applications.
With so much valuable information flowing through a single integration point, the risks are high. Here are some of the common threats that iPaaS environments face:
Data Breach
These are performed by unauthorized people accessing sensitive data that can cost us both money and reputation.
Data breaches can occur through hacking, phishing, or exploiting software vulnerabilities. United States Data breach costs US organizations $9.48 million on average in 2023 alone—this is the average cost of a data breach. These costs are associated with legal fees, fines, potential loss of business as well the detriment to the brand and reputation.
API Vulnerability
APIs are the heart of iPaaS, which establishes communication between multiple systems. But when they are not properly secured, they can become a major area of vulnerability.
Attackers can use a variety of methods to exploit your API and gain access to data, poorly patched services, or inject malicious code.
In the first half of 2022, API attacks surged by a staggering 681%, according to a study released in late September from Salt Security showing just how much more at risk we have become due to unprotected APIs.
Insider Threats
Those employees or contractors who have access to the iPaaS platform can deliberately take advantage of data security.
Insider threats can come in a variety of shapes and flavors, from angry employees working destruction, to careless members of staff leaking your data all over the place. Or it could be your credentials that were compromised.
Verizon’s 2023 report released this month said that insiders were involved in a separate 19% of data breach incidents, again underlining the importance of tight access controls and employee training.
How Can You Protect Your Data?
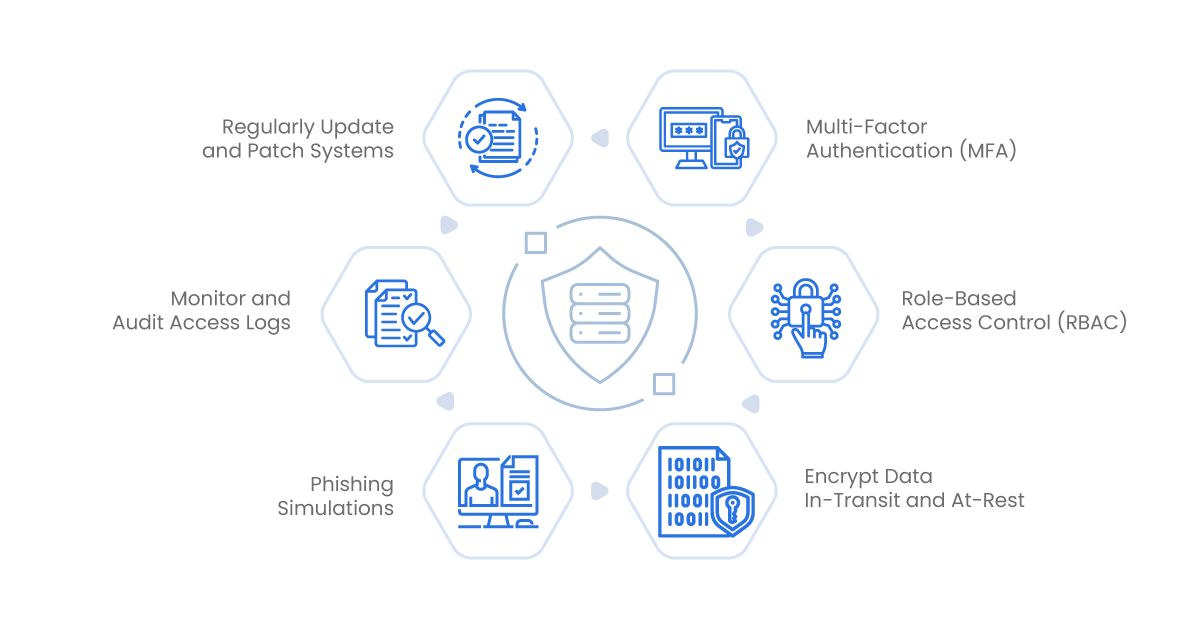
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a critical step in securing your iPaaS environment.
MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing the platform. This frequently consists of a mix of the user’s know-how (for example, passwords), identity (like biometric data), and possessions (security tokens, smartphones, etc.).
MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access by adding additional layers of security. Even if an attacker manages to obtain a user’s password, they would still need the second or third factor to gain entry. This method is particularly effective against phishing attacks, where credentials might be stolen, as MFA ensures that stolen passwords alone are not enough to compromise accounts.
According to Microsoft, MFA can prevent up to 99.9% of automated attacks. This statistic highlights the effectiveness of MFA in protecting against a wide range of threats, including phishing attacks and brute force attacks.
An Example: A SaaS provider implementing iPaaS to integrate various customer management systems uses MFA to protect its administrative portal. This approach ensures that even if an employee’s login credentials are compromised, the attacker would also need the employee’s phone for the second authentication factor, thus safeguarding sensitive configuration settings and customer data.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is useful for managing user permissions and access within an iPaaS environment.
RBAC assigns permissions based on user roles, which are predefined according to the user’s job function within the organization. This means users can only access data and functionalities relevant to their specific roles, which helps in minimizing the risk of insider threats and data misuse.
RBAC ensures that users have appropriate access rights without over-permission. This practice is crucial in maintaining data integrity and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
RBAC can also simplify administrative tasks by automating permission management based on role changes or user transitions.
An Example: A financial institution employs iPaaS to integrate its core banking system with transaction processing systems and customer service platforms.
By implementing RBAC, the institution ensures that tellers only have access to customer account details and transaction records, while auditors can access comprehensive transaction histories and compliance reports. This role-based segregation of data access helps protect against internal fraud and errors.
Encrypt Data In-Transit and At-Rest
Encryption is a fundamental security measure that safeguards data from unauthorized access by encoding it into a format that can only be read or deciphered by those with the correct decryption key.
In-Transit Encryption:
This involves encrypting data as it travels between systems, ensuring it remains confidential and intact during transmission. Protocols such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) are commonly used to secure data in transit, protecting it from interception or tampering by malicious actors.
An Example: An e-commerce company using iPaaS to synchronize data between its online store, inventory management system, and third-party logistics providers employs in-transit encryption to secure customer payment information during transmission. This ensures that sensitive customer data, such as credit card details and shipping addresses, is protected from interception during data exchanges.
At-Rest Encryption:
This protects data that is stored on servers or within databases. By encrypting data at rest, organizations ensure that even if the physical storage infrastructure is compromised, the data remains secure and inaccessible without the proper decryption credentials.
According to a 2022 report by Cybersecurity Ventures, the global cost of cybercrime is expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This staggering figure underscores the importance of robust encryption practices, both in-transit and at-rest, to protect valuable data and mitigate the risks associated with cyber threats.
An Example: A global manufacturing company uses iPaaS to integrate its product design, supply chain management, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. By applying at-rest encryption, the company ensures that proprietary design documents, supplier contracts, and financial records are securely stored, even if their cloud storage provider experiences a security breach.
Aonflow is the leading integration platform.
You can kick-start by integrating your first-ever workflow in just a matter of minutes.
Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Regularly updating and patching systems is essential to protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. This includes applying software updates and security patches to the iPaaS platform and all connected systems.
Automated Updates:
Configuring automated updates ensures that the iPaaS platform receives the latest security patches and enhancements without manual intervention, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities being exploited due to outdated software.
An Example: A global retail chain uses iPaaS to integrate its inventory management system with its e-commerce platform and supply chain solutions. To maintain security, the company schedules automated updates for the iPaaS platform to ensure it is always running the latest version with the most recent security patches. Regular vulnerability scans are conducted to detect and address any security gaps promptly.
Vulnerability Management:
Regularly scanning for and addressing vulnerabilities helps identify and mitigate potential security risks before they can be exploited by attackers.
Monitor and Audit Access Logs
Proactive monitoring and auditing of access logs are vital for identifying and responding to security incidents.
Continuous Monitoring:
Implementing continuous monitoring systems helps detect unusual activities and potential security breaches in real time. This allows for immediate responses to any suspicious behavior or unauthorized access attempts.
An Example: A healthcare organization leverages iPaaS to connect various patient care systems and administrative tools. The organization implements continuous monitoring to detect any unusual access patterns or data access anomalies. Regular audits of access logs help ensure that only authorized personnel access patient records and that any unauthorized access attempts are promptly investigated and addressed.
Regular Audits:
Regular audits of access logs help ensure compliance with security policies and procedures and identify any discrepancies or policy violations that need to be addressed.
A study by IBM Security in 2020 found that companies with fully deployed security automation saved an average of $3.58 million per breach compared to those without.
Educate and Train Employees
Since human mistake plays a major role in many security breaches, staff education and training are essential.
Security Training Programs:
Developing comprehensive security training programs helps employees understand the importance of data protection and the best practices for maintaining security.
An Example: A technology firm using iPaaS to manage internal communications and project management tools implements regular security training sessions for all employees. The firm also conducts phishing simulations to prepare staff to identify and handle phishing attempts, reducing the likelihood of successful attacks and enhancing overall security posture.
Phishing Simulations
Phishing simulations are an effective way to educate employees about the dangers of phishing attacks and to enhance their ability to recognize and respond to phishing attempts. These simulations involve sending simulated phishing emails or messages to employees to test their ability to identify suspicious or fraudulent content.
Importance of Phishing Simulations:
One frequent type of cyberattack is phishing. Attackers lure people into disclosing sensitive information, including login passwords or financial information, by sending them misleading emails or texts. These attacks can have severe consequences, including data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage.
By conducting phishing simulations, organizations can:
- Raise Awareness: Educate employees about the characteristics of phishing attempts, including common tactics, such as urgent language, suspicious links, or unexpected attachments.
- Improve Detection Skills: Help employees practice identifying phishing attempts in a controlled environment, improving their ability to recognize and report real threats.
- Strengthen Incident Response: Enhance employees’ readiness to respond to phishing attempts by providing them with clear procedures for reporting suspicious emails and handling potential security incidents.
Example 1: A financial services company implements phishing simulations to train its employees on how to handle phishing attempts. The simulations are designed to mimic common phishing tactics used in the financial industry, such as fake account verification requests or fraudulent investment opportunities.
Employees who fall for the simulated phishing emails receive immediate feedback and additional training resources, helping them improve their skills and reduce the risk of falling victim to real phishing attacks.
Example 2: An educational institution uses phishing simulations as part of its cybersecurity awareness program. The institution sends simulated phishing emails to faculty and staff, including fake alerts about password expiration or account issues.
After the simulation, the IT department reviews the results and conducts follow-up training sessions to address any gaps in knowledge and reinforce best practices for recognizing and handling phishing attempts.
Example 3: A healthcare provider conducts regular phishing simulations to protect sensitive patient information. The simulations are tailored to reflect phishing scenarios relevant to the healthcare sector, such as fake emails requesting patient data updates or fraudulent communications from supposed regulatory bodies.
By regularly testing employees’ ability to spot phishing attempts, the provider ensures that staff remain vigilant and can effectively safeguard patient data from cyber threats.
Conclusion
As we all know, the need for securing your online environment is now more significant than ever in light of happenings that data breaches are progressively becoming sophisticated and no longer ordinary cyber threats.
This means ensuring that you have strong authentication and authorization, encrypted data at rest or in transit, systems are up to date with security patches applied regularly (CVE listings), managing access logs, and educating employees on the importance of security.
Keep up with these iPaaS security best practices, and take a proactive stand in the defense of your organization’s important data.
Aonflow iPaaS – Free for First 3 Months!
Build and run up to 1,500 transactions monthly with no cost. No payment info needed!